Trust.
Innovation.
Solutions
Solutions
Products Sustainability Contact
Reliable Solutions.
Fiberr
Fiberr
R&D Production career
FIBERR
Innovative Solutions for You.
Review All Our Products. Find the Right Solution for Your Projects.
fıberr
Solutions
Security
Fiberr offers GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) products specifically designed to meet security needs.
Railing
Fiberr’s GRP fences not only increase safety, but also provide an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Architectural Applications
Fiberr offers specialized GRP solutions for architectural projects, combining functionality and safety.
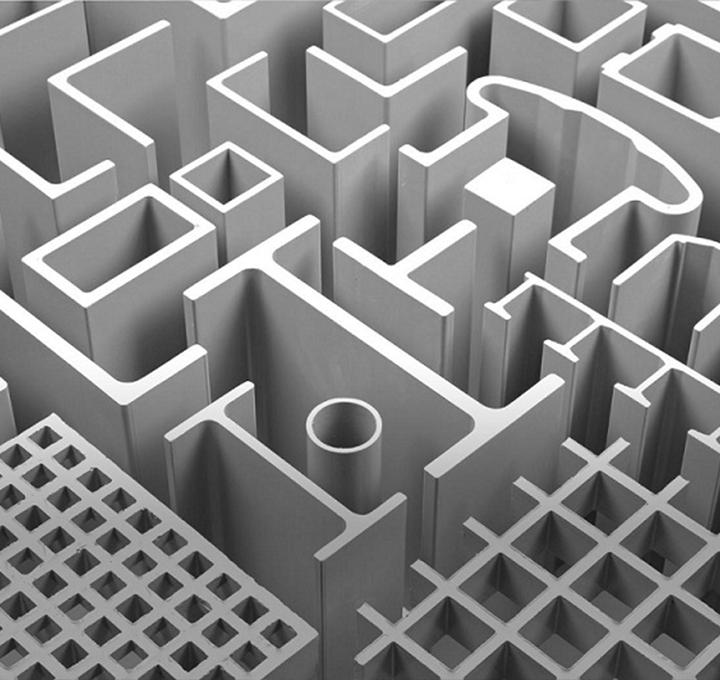
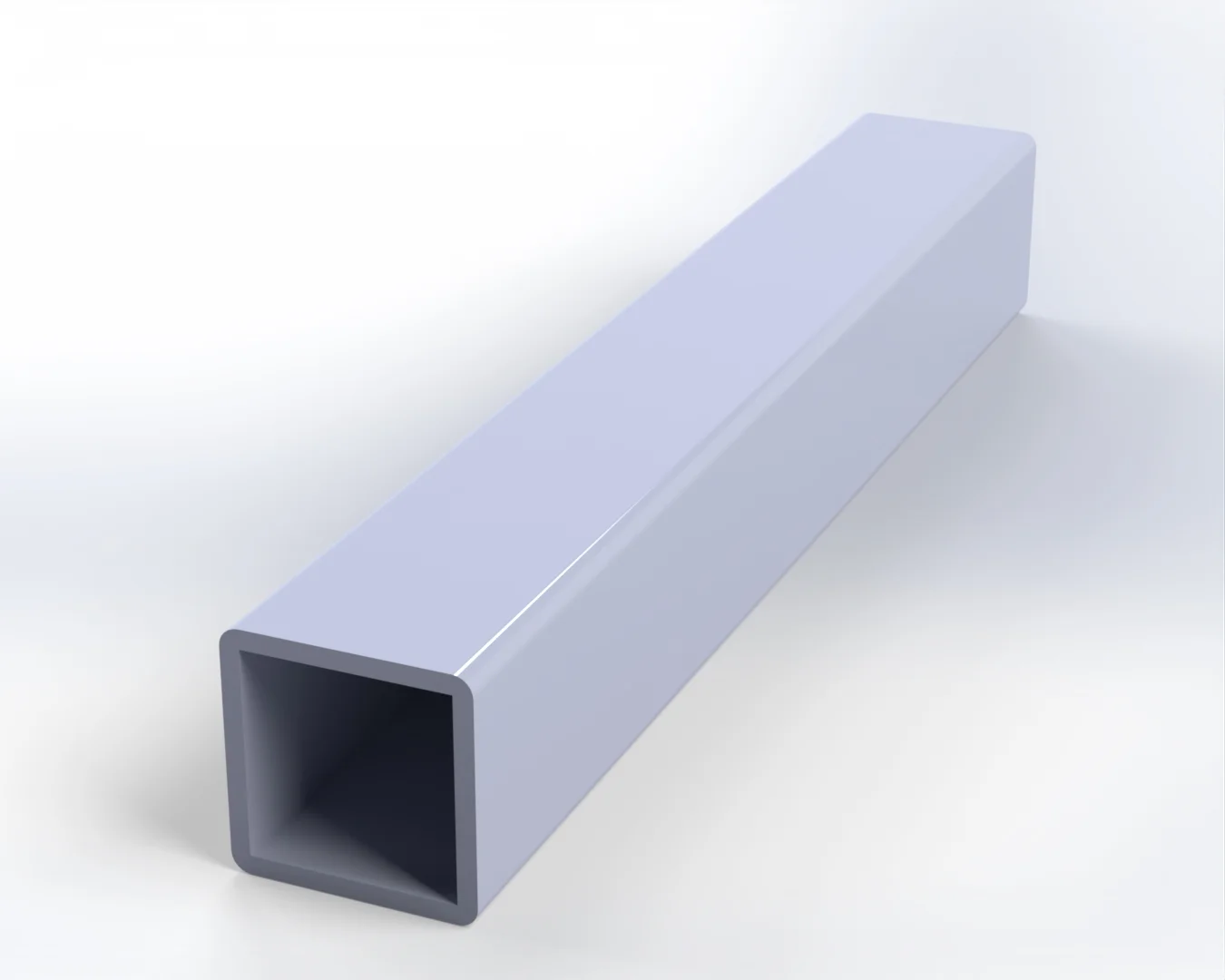
BMC-SMC
BMC and SMC are both fiber-reinforced materials and are typically manufactured using glass stranded fibers of different lengths
Stairs
Fiberr’s GRP stair solutions enable the construction of safe and durable structures.
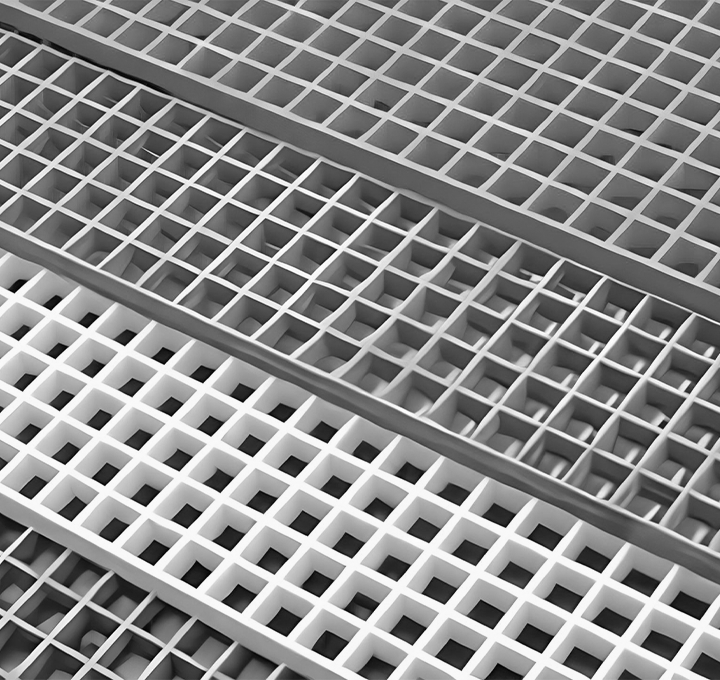
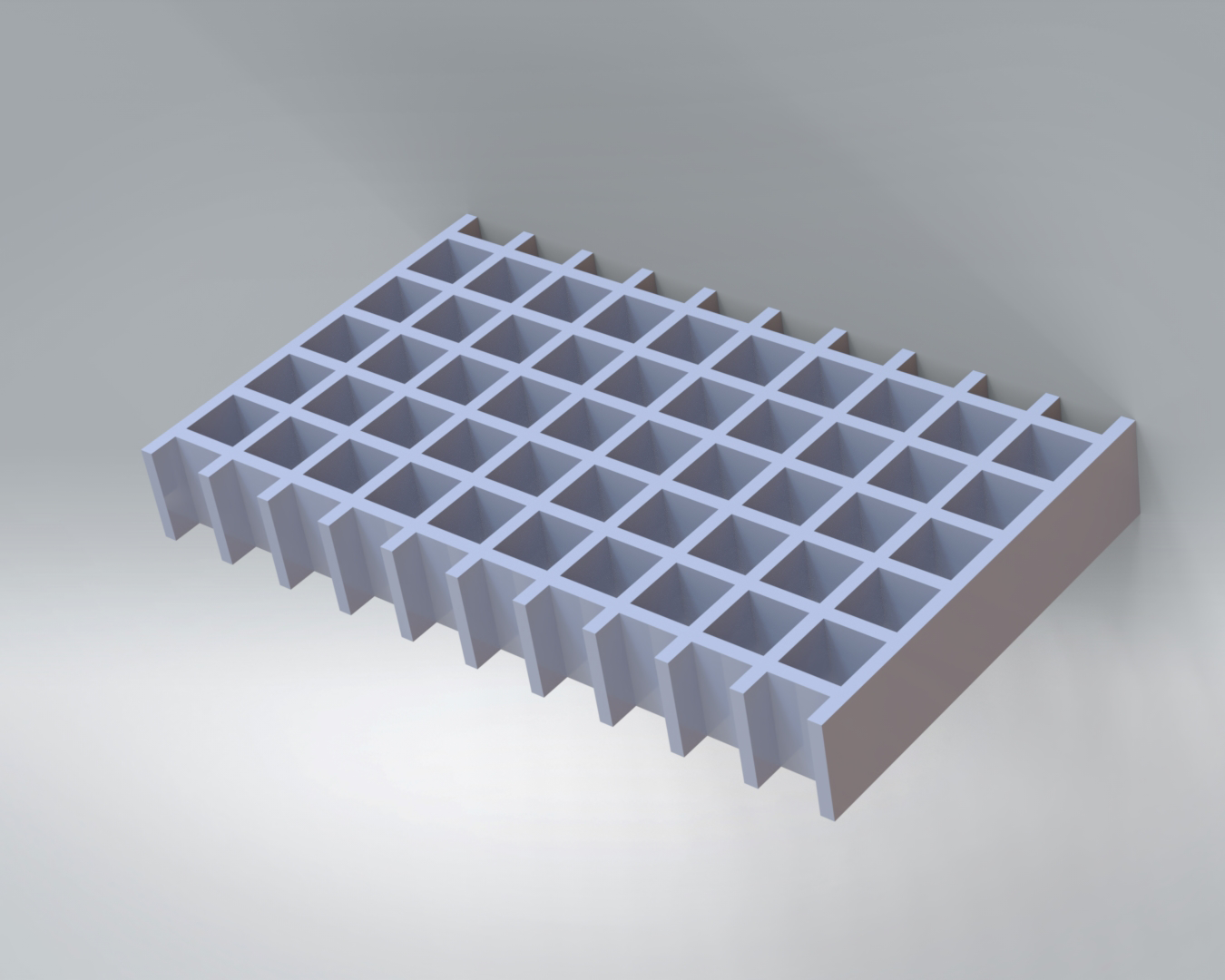
Platform
Fiberr’s GRP bridges provide a reliable solution for construction projects with their high load-bearing capacity and lightweight structure.
Security
Fiberr offers GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) products specifically designed to meet security needs.
Railing
Fiberr’s GRP fences not only increase safety, but also provide an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Architectural Applications
Fiberr offers specialized GRP solutions for architectural projects, combining functionality and safety.
BMC-SMC
BMC and SMC are both fiber-reinforced materials and are typically manufactured using glass stranded fibers of different lengths
Stairs
Fiberr’s GRP stair solutions enable the construction of safe and durable structures.
Platform
Fiberr’s GRP bridges provide a reliable solution for construction projects with their high load-bearing capacity and lightweight structure.
Security
Fiberr offers GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) products specifically designed to meet security needs.
Railing
Fiberr’s GRP fences not only increase safety, but also provide an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
products
Powerful Design Long Lasting Performance!

fıberr
Figures Leaving Traces to the Future with Fiberr